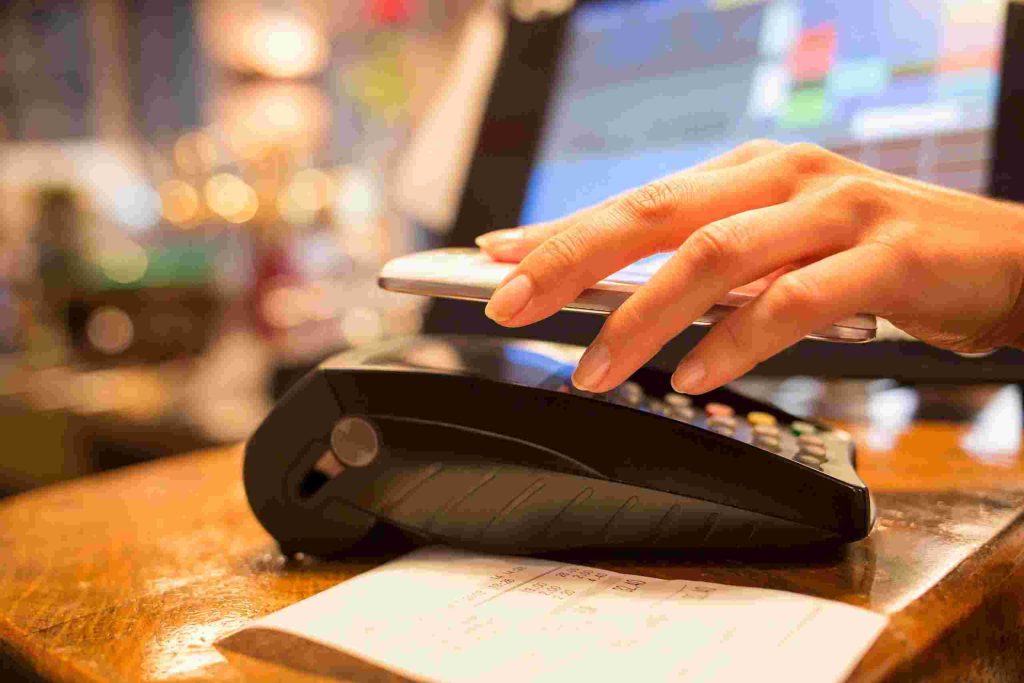
What is NFC?
Near Field Communication NFC is the abbreviation of Near Field Communication, which is short-range wireless communication technology. .
NFC provides a simple, touch-sensitive solution that allows consumers to exchange information and access content and services simply and intuitively. This technology evolved from contactless radio frequency identification (RFID) and is backward compatible with RFID. It was first promoted by Philips, Nokia and Sony, and may be mainly used in handheld devices such as mobile phones. Due to the natural security of near field communication, NFC technology is considered to have great application prospects in fields such as mobile phone payment. NFC combines contactless reader, contactless card and peer-to-peer functionality into a single chip, opening up countless new opportunities for consumers’ lifestyles.
It is an open interface platform for fast, proactive setup of wireless networks and a virtual connector for existing cellular, Bluetooth and wireless 802.11 devices. Unlike RFID, NFC uses two-way identification and connection. Operates in the 13.56MHz frequency range within a 20cm distance. It can quickly and automatically establish a wireless network, providing a “virtual connection” for cellular devices, Bluetooth devices, and Wi-Fi devices, enabling electronic devices to communicate over short distances.
What are the NFC applications?
Applications of NFC technology can be divided into four basic categories:
(1) Touch and Go, such as access control, tickets and tickets, etc., the user only needs to bring the mobile device that stores the ticket or door control password close to the reading device.
(2) Touch and Confirm, such as mobile payment, the user confirms the transaction by entering the password or just accepting the transaction.
(3) Touch and Connect, such as connecting two devices with built-in NFC for point-to-point data transmission, such as downloading music, transferring pictures, and synchronously exchanging address books.
(4) Touch and Explore: NFC devices can provide more than one useful function, and consumers will be able to browse an NFC device to understand what functions and services are provided.
Types of nfc tags ?
NFC Type 1
Based on ISO 14443 A and is currently available exclusively from Innovision Research & Technology (Topaz™). It has a 96-byte memory capacity, which makes it a very cost-efficient tag for a wide range of NFC applications
NFC Type 2
Based on ISO 14443 A and is currently exclusively available from Philips (MIFARE UltraLight). It has half the memory capacity of Type 1 tags
NFC Type 3
Based on FeliCa and is currently exclusively available from Sony. It has a larger memory (currently 2kbyte) and operates at a higher data rate (212kbit/s), which means it is suitable for more complex applications
NFC Type 4
Its fully compatible with ISO 14443A/B and is available from a number of manufacturers, including Philips (typical product example is MIFARE DESFire). It offers large memory-addressing capability with read speeds of between 106kbit/s and 424kbit/s – making it suitable for multiple applications.
NFC Type 5
Based on ISO/IEC 15693 specification. The ISO/IEC 15693 specification was originally developed to achieve long RF operating ranges of up to 1.5 meters. The NFC Forum has chosen to support an active communication mode that allows data transfer performance similar to the RFID technology supported by the NFC Forum, but limits the read distance of NFC devices. Typical tag type 5ICs are the Enzhi ICode series and the ST25TV series by ST Microelectronics. Applications for label type 5 are typically library books, packaging, and ticketing, etc.
| NFC Forum Platform | Compatible Products |
| NFC Forum Type 1 Tag | Innovision Topaz |
| NFC Forum Type 2 Tag | NTAG213/215/216 NXP MIFARE Ultralight NXP MIFARE Ultralight EV1 NXP MIFARE Ultralight C |
| NFC Forum Type 3 Tag | Sony Felica |
| NFC Forum Type 4 Tag | NXP DESFire Series NXP SmartMX with JCOP |
| NFC Forum Type 5 Tag | NXP ICode Series ST25TV Series |
Contact Form
We can help you?
Share this page